What is instrumentation? A Complete Guide

What is instrumentation about?
Instrumentation is all about process and control. It is the nervous system that drives any industrial, manufacturing, commercial process.
The instrumentation allows for automation and scalability techniques to scale their products safely, efficiently and effectively.
In a process plant, instruments and instrumentation are very important for control systems or automation in industrial processes. Users will find many ways to control using instrumentation by sending signals from field instruments to the Control system such as PLC or DCS system.
The basic objective of instrumentation is to obtain the maximum output from industry with minimum raw material usage. It helps in optimum utilization of raw materials and improves efficiency in processes.
Instrumentation is an automated form of measurements and control in physical properties such as flow, pressure, temperature, and level, density, gas analyzers, water analyzer (like PH) and etc.
The block diagram of a simple Instrumentation Control System:
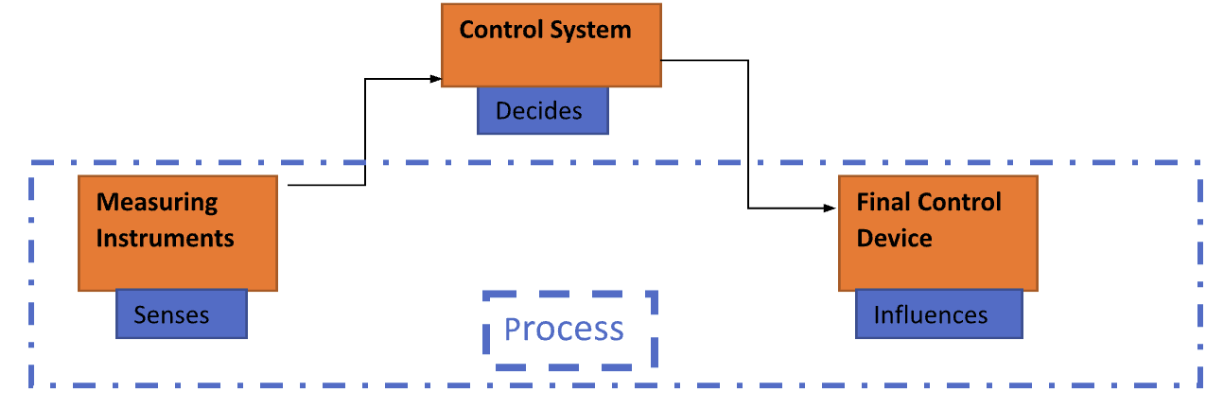
Based on the Diagram anything which cannot be measured cannot be controlled. After the quantity has been measured a signal representing this quantity is then transmitted to an indication or computing device where either manual or automated action takes place.
If the controlling action is automated the computer sends a signal to the final controlling device which then influences the quantity being measured. This final control device can be a control valve, electric motor or electric heater.
Both measuring instrument and Final Control Device are connected to the same process.
Variable process of instrumentations:
The variable process of instrumentations is as fallow:
-
Flow measurement:
Any fluids or liquids flowing from one place to another place is known as flow. It is defined as volume per unit: L/S, L/M, m3/h, Kg/h etc. Some examples of instruments which work this way are:
Magnetic Flow meter, Rotameter, Thermal flow meter, Vortex Flow meter
-
Pressure:
Force per unit: Bar, Pa, inches H2O, mm H2O the instruments in this case are named also as: Pressure Switch, Pressure Transmitter, Differential Pressure transmitter, Pressure Gauge etc.
-
Temperature:
Centigrade, Degree Fahrenheit, Degree Kelvin such as: Temperature Gauge, Temperature Transmitter RTD, Temperature Transmitter Thermocouple
-
Level measurement:
It is a technique to measure the level of surface inside a tank, reactor or vessel.
Unit are defined as Meters, mm, cm, percentage, Capacitance Level Switch, ELECTRODE Level Switch, FLOAT Level Switch, MAGNETIC Level Transmitter, RADAR Level Transmitter, ULTRASONIC Level Transmitter
-
Gas Analyzer:
Analyzing and measuring the volume of gases through the pipe line or an exhausted line. Units are defined as percentage, ppm, etc.
Instrument or Instrumentation?
What actually exists between the instrumentation and instruments is that, in fact, measuring instruments form part of a far wider concept identified as instrumentation. This large class, on the other hand, is identified due to their being precisely those devices or systems that ideally carry out the entire procedure of instrumentation effective and efficiently.
FAQs:
Why are instrumentations an important part of a plant?
Instrumentation is the means of increasing the industrial output with the lowest use of raw materials. Instrumentation optimizes raw material usage and increases process efficiency.
What is the difference between instrument and instrumentation?
The distinction between instrumentation and measurement tools is that measurement tools are actually part of a broader concept known as instrumentation, which is recognized as the devices that carry out the instrumentation process.